User Guide
UNIon is a desktop app for organizing various types of contacts, optimized for use for the vast majority of computing students. If you are already familiar with Unix commands, then UNIon will be easy for you to use.
- Quick start
- Features
- FAQ
- Command summary
Quick start
- Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer - Download the latest JAR file from here
- Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your UNIon
- Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds, and it should look similar to this image below. Note how the app contains some sample contacts
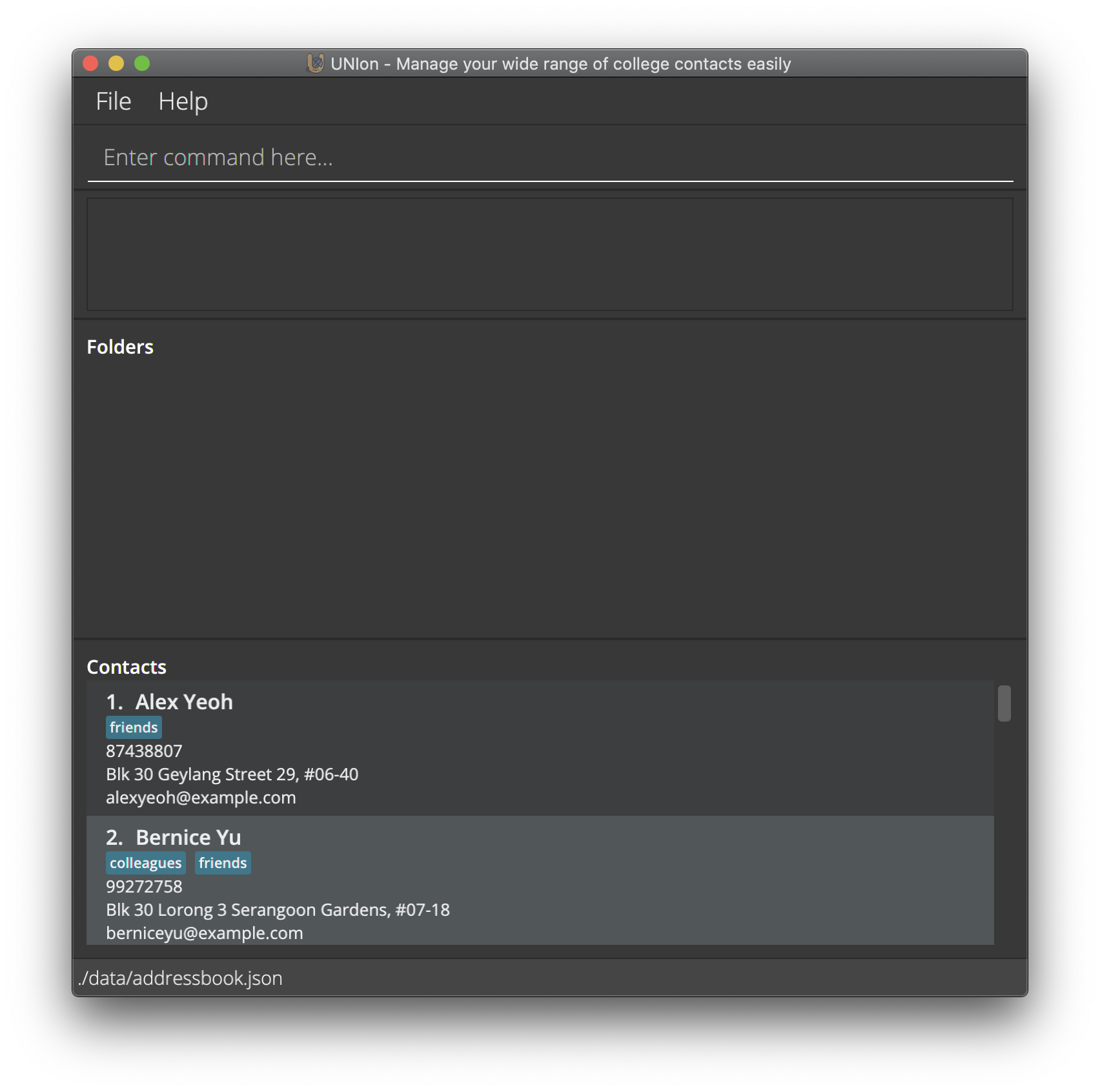
- Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
ls -contacts: Lists all contacts -
touch -n John Doe -p 98765432 -e johnd@example.com -a John street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto UNIon -
rm 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list -
rm -contacts: Deletes all contacts -
exit: Exits the app
-
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user
e.g. intouch -n NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used astouch -n John Doe -
Items in square brackets are optional
e.g.-n NAME [-t TAG]can be used as-n John Doe -t friendor as-n John Doe -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times
e.g.[-t TAG]…can be used as-t friend,-t friend -t familyetc -
Parameters can be in any order
e.g. if the command specifies-n NAME -p PHONE,-p PHONE -n NAMEis also acceptable -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken
e.g. if you specify-p 12341234 -p 56785678, only-p 56785678will be taken -
For commands that do not take in parameters (such as
helpandexit) , extraneous parameters will be ignored
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp -
Flags such as
-contactsand-foldersare part of the command word and must be placed immediately after the main command word
e.g. (ls -contactsnotls -invalid_flag -contacts)
Viewing help: help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
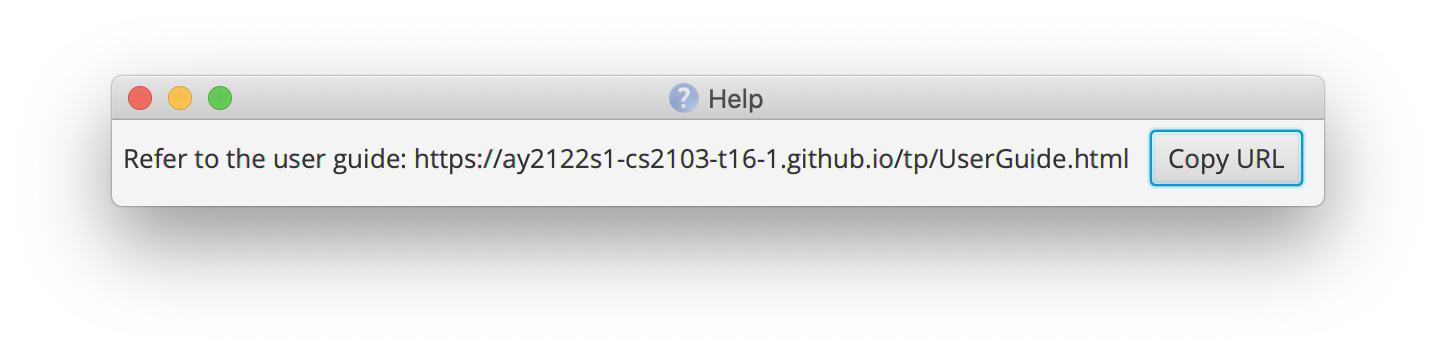
Format: help
Managing contacts
Adding a contact: touch
Adds a contact to UNIon.
Format: touch -n NAME -p PHONE -e EMAIL -a ADDRESS [-t TAG]…
-
NAMEhas a character limit of 70 characters -
NAMEis case-sensitive as John Doe and john doe will be treated as different contacts -
PHONEaccepts any length to allow for phone formats from different countries -
ADDRESSis truncated by an ellipsis if the contents cannot fit in one line - Duplicate
TAGs are ignored - We recommend that
TAGs are kept to a maximum of 50 characters. If a tag has more than 50 characters, you may not be able to view the entire tag (depending on the size of the window)
Examples:
touch -n John Doe -p 98765432 -e johnd@example.com -a John street, block 123, #01-01touch -n Betsy Crowe -t friend -e betsycrowe@example.com -a Newgate Prison -p 1234567 -t criminal
Listing all contacts: ls -contacts
Shows a list of all contacts in UNIon.
Format: ls -contacts
Editing a contact: vim
Edits an existing contact in the UNIon.
Format: vim INDEX [-n NAME] [-p PHONE] [-e EMAIL] [-a ADDRESS] [-t TAG]…
- Edits the contact at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed contact list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided
-
NAMEhas a character limit of 70 characters -
PHONEaccepts any length to allow for phone formats from different countries -
ADDRESSis truncated by an ellipsis if the contents cannot fit in one line - Duplicate
TAGs are ignored - We recommend that
TAGs are kept to a maximum of 50 characters. If a tag has more than 50 characters, you may not be able to view the entire tag (depending on the size of the window) - Existing values will be updated to the input values
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the contact will be removed i.e. adding of tags is not cumulative
- You can remove all the contact’s tags by typing
-twithout specifying any tags after it
Examples:
-
vim 1 -p 91234567 -e johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st contact to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively -
vim 2 -n Betsy Crower -tEdits the name of the 2nd contact to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags
Locating contacts by name: find -contacts
Finds contacts whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find -contacts KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Contacts matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch) e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang - All flags after
-contactswill be ignored e.g.find -contacts -invalid_flag Hansis equivalent tofind -contacts Hans
Examples:
-
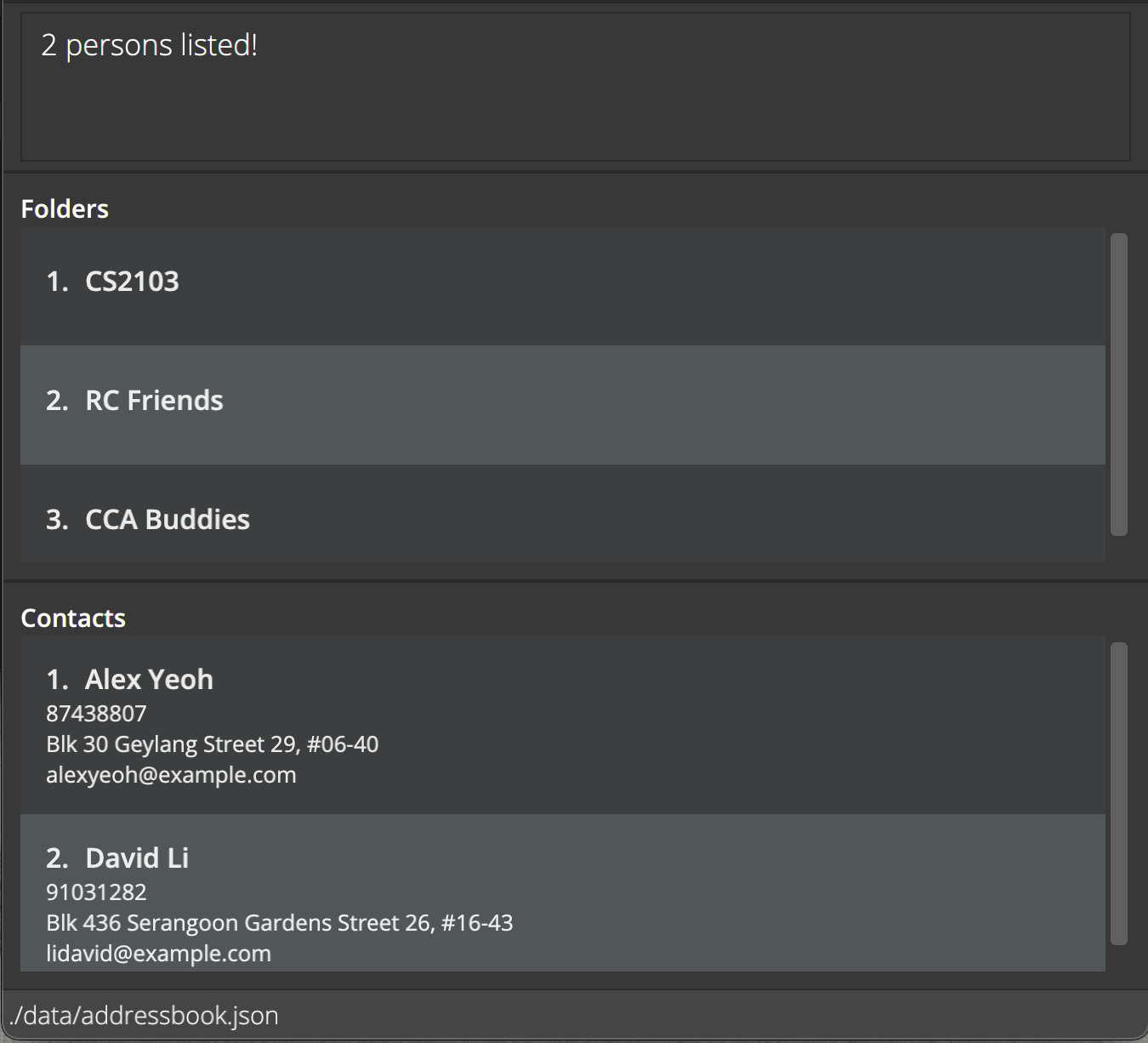
find -contacts JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find -contacts alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
Deleting a contact: rm
Deletes the specified contact from UNIon.
Format: rm INDEX
- Deletes the contact at the specified
INDEX - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed contact list
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
ls -contactsfollowed byrm 2deletes the 2nd contact in UNIon -
find -contacts Betsyfollowed byrm 1deletes the 1st contact in the results of thefind -contactscommand
Clearing all contacts: rm -contacts
Clears all contacts from UNIon.
Format: rm -contacts
Managing folders
Adding a folder: mkdir
Creates a folder for contacts to be added into.
Format: mkdir FOLDER_NAME
- Creates a folder with the name
FOLDER_NAME -
FOLDER_NAMEhas a maximum character limit of 30 - Duplicate folder names are not allowed
Examples:
-
mkdir CS2103creates a folder with the nameCS2103
Adding contacts to a folder: echo
Adds existing contacts into a folder.
Format: echo INDEX [INDEX]... >> FOLDER_NAME
- Adds the contacts at the specified indices into the given folder. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed contact list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
-
INDEXmust be a valid index referring to an existing contact in the current list of contacts shown -
INDEXmust not already be in the folder - If multiple
INDEXare passed, they must be unique and cannot contain duplicates -
FOLDER_NAMEmust be an existing folder
Examples:
-
echo 3 >> CS2103Adds contact 3 to CS2103 folder -
echo 3 4 1 9 10 >> CS2103Add contacts 3, 4, 1, 9, 10 to CS2103 folder
Deleting a contact from folder: rm
Deletes the specified contact from the list of contacts from the folder.
Format: rm INDEX >> FOLDER_NAME
- Deletes contact at
INDEXas seen on the contact list from the folder namedFOLDER_NAME
Examples:
-
rm 1 >> CS1010deletes a contact that corresponds to index 1 in the contact list from the folderCS1010
Listing all folders: ls -folders
Retrieves list of all folders created.
Format: ls -folders
Editing a folder name: mv
Replaces the old folder name with the new folder name.
Format: mv OLD_FOLDER_NAME | NEW_FOLDER_NAME
-
NEW_FOLDER_NAMEhas a maximum character limit of 30
Locating folders by name: find -folders
Finds folders whose name contains any of the given keywords.
Format: find -folders KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g.
cs2103will matchCS2103 - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Team Project CS2103will matchCS2103 Team Project - Partial words will be matched e.g.
CSwill matchCS2103andCS2101 - Folders matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.CS2103 Team Projectwill returnCS2103,Team Project - All flags after
-folderswill be ignored e.g.find -folders -invalid_flag CS2103is equivalent tofind -contacts CS2103
Examples:
-
find -folders CSreturnsCS2103andCS2101 -
find -folders CS2103 Team ProjectreturnsCS2103,Team Project
Deleting a folder: rmdir
Deletes a specified folder
Format: rmdir FOLDER_NAME
- Deletes folder with the name
FOLDER_NAME
Examples:
-
rmdir CS1010deletes a folder with the nameCS1010
Clearing all folders: rm -folders
Clears all folders from UNIon.
Format: rm -folders
Exiting the program: exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
UNIon data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
UNIon data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app on the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous UNIon home folder.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Help | help |
| Add new contact |
touch -n NAME -p PHONE -e EMAIL -a ADDRESS [-t TAG] e.g., touch -n James Ho -p 22224444 -e jamesho@example.com -a 123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 -t friend -t colleague
|
| List contacts | ls -contacts |
| Edit contact |
vim INDEX [-n NAME] [-p PHONE] [-e EMAIL] [-a ADDRESS] [-t TAG] e.g., vim 2 -n James Lee -e jameslee@example.com
|
| Find contact |
find -contacts KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find -contacts James Jake
|
| Delete contact |
rm INDEXe.g., rm 3
|
| Clear contacts | rm -contacts |
| Add new folder |
mkdir FOLDER_NAME e.g. mkdir CS2103
|
| Add contact to folder |
echo INDEX >> FOLDER_NAME e.g., echo 3 >> CS2103
|
| Add multiple contacts to folder |
echo INDEX [INDEX]... >> FOLDER_NAME e.g. echo 3 4 1 9 10 >> CS2103
|
| Delete contact from folder |
rm INDEX >> FOLDER_NAME e.g., rm 1 >> CS2102
|
| List folders | ls -folders |
| Edit folder name |
mv OLD_FOLDER_NAME | NEW_FOLDER_NAME e.g., mv CS2103 | CS2102
|
| Find folders |
find -folders KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find -folders CS2103
|
| Delete folder |
rmdir FOLDER_NAME e.g., rmdir CS1010
|
| Clear folders | rm -folders |